Explore every aspect of varicocele in adolescents symptoms to watch for, and the expert guidance
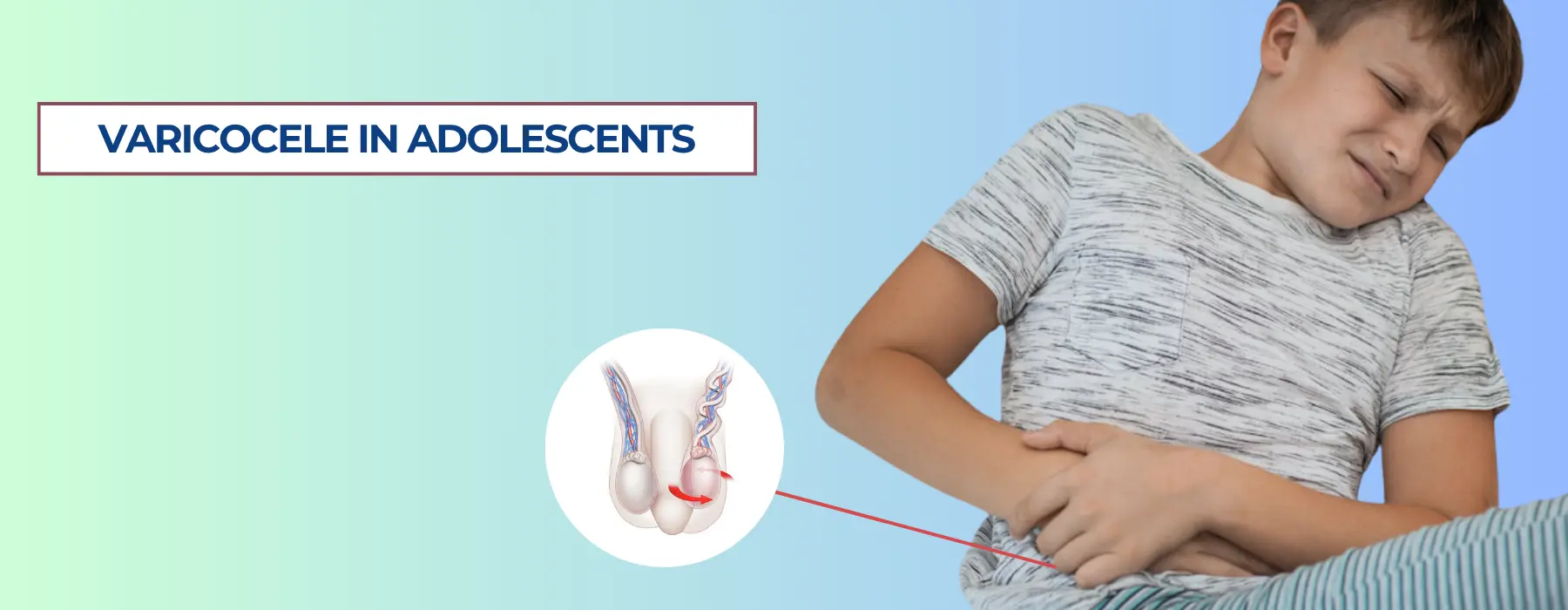
Varicocele in adolescents is a condition that often goes unnoticed in its early stages but can have long-term implications for male reproductive health. Affecting nearly 15% of adolescent boys, varicoceles are abnormally enlarged veins within the scrotum, similar to varicose veins that occur in the legs. While often painless, they can lead to discomfort, testicular atrophy, or even fertility issues later in life if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnostic process, and the best treatment options is essential for parents and teens alike.
In this blog, we’ll explore every aspect of varicocele in adolescents and highlight expert guidance from Dr. Santosh Patil – Best Vascular Surgeon in Pune, who offers advanced, minimally invasive treatment options tailored to young patients.
What Is Varicocele?
A varicocele is a swelling of the veins (pampiniform plexus) in the scrotum, caused by poor functioning of the valves within the veins. These valves are supposed to ensure one-way blood flow back to the heart, but when they fail, blood pools in the veins, causing them to enlarge. This venous congestion increases pressure and can lead to testicular damage over time.
Why Varicoceles Matter in Adolescents
Adolescents are in a critical phase of physical and hormonal development. During puberty, the testes grow and mature rapidly. A varicocele, if significant, can impair this growth by affecting blood circulation and oxygen delivery to the testicles. Early detection and intervention are crucial to prevent long-term consequences like reduced fertility or testicular shrinkage.
Causes of Varicocele in Adolescents
While the exact cause is not always known, several anatomical and physiological factors contribute to the development of varicocele in adolescents:
- Faulty venous valves: Incompetent valves allow blood to backflow into the scrotal veins.
- Anatomical asymmetry: The left testicular vein drains at a sharper angle, making left-sided varicoceles more common.
- Rapid growth during puberty: Increased blood flow and hormonal changes may exacerbate the problem.
Common Symptoms of Adolescent Varicocele
Many adolescents may not experience noticeable symptoms. However, some may report:
- Dull ache or heaviness in the scrotum
- Visible or palpable twisted veins
- Size difference between the two testicles
- Pain that worsens with standing or physical activity
- Testicular atrophy (shrinkage)
How Is Varicocele Diagnosed?
Dr. Santosh Patil emphasizes that diagnosis is often clinical, supported by imaging when needed. Diagnosis involves:
- Physical Examination: The doctor palpates the scrotum while the patient stands, sometimes asking them to perform a Valsalva maneuver (bearing down) to make the varicocele more prominent.
- Scrotal Ultrasound: This is the most accurate imaging tool for confirming the diagnosis, assessing vein diameter, and checking for testicular volume loss.
Varicoceles are graded according to severity:
- Grade 1: Small; felt only during a Valsalva maneuver.
- Grade 2: Medium; palpable without Valsalva but not visible.
- Grade 3: Large; visible and palpable.
Early-grade varicoceles may be monitored, while larger ones often require treatment, especially if symptoms or testicular shrinkage are present.
Best Treatment Options for Varicocele in Adolescents
Dr. Santosh Patil – Best Vascular Surgeon in Pune specializes in both conservative and advanced treatments for adolescent varicocele. The best treatment depends on the severity and impact of the condition.
1. Observation
For small, asymptomatic varicoceles with no testicular growth disturbance, observation with regular follow-ups and ultrasounds may be recommended.
2. Surgical Options
Surgery is typically considered when:
- Testicular atrophy is present
- There is scrotal pain
- Fertility may be compromised
Common surgical options include:
Microsurgical Varicocelectomy: Considered the gold standard. Involves tying off the enlarged veins while preserving the artery and lymphatics. Low recurrence and complication rates.
Laparoscopic Varicocelectomy: Minimally invasive and effective, especially when both sides are affected.
3. Varicocele Embolization (Minimally Invasive)
Offered by Dr. Santosh Patil, this non-surgical method uses imaging guidance to insert a catheter into the groin vein. A coil or sclerosing agent is used to block the affected veins.
Advantages include:
- No surgical incision
- Short recovery time
- Performed under local anesthesia
This technique is increasingly preferred for adolescents with high-grade varicoceles who want to avoid surgery.
Recovery After Varicocele Treatment
Whether undergoing surgery or embolization, adolescents can expect:
- Mild discomfort for a few days
- Return to light activity within a week
- Full recovery and sports participation in 2–3 weeks
Dr. Santosh Patil ensures that patients and parents receive complete post-procedure care instructions, ensuring safe and fast healing.
As the Best Vascular Surgeon in Pune, Dr. Santosh Patil is trusted by families for his clinical excellence and patient-centered care.
- Expertise in adolescent vascular health
- Offers both surgical and non-surgical treatments
- Modern, USG-guided diagnosis and minimally invasive therapy
- High patient satisfaction with minimal recurrence
Conclusion
Varicocele in adolescents is a common yet often overlooked condition that can significantly impact testicular development and future fertility. Early diagnosis, expert evaluation, and timely treatment can make a world of difference. With minimally invasive techniques and compassionate care, Dr. Santosh Patil ensures the best outcomes for young patients in Pune.
If your child shows symptoms of scrotal discomfort or you suspect a varicocele, book a consultation today with Pune’s most trusted vascular surgeon.
